Medulloblastoma Brain Cancer Overview – Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, and Survival
Medulloblastoma is a fast-growing, high-grade brain tumor that originates in the cerebellum, the lower back part of the brain that controls balance, coordination, and fine motor skills. This aggressive type of cancer most commonly affects children, accounting for approximately 20% of all pediatric brain tumors. However, it can also occur in adults, though much less frequently.
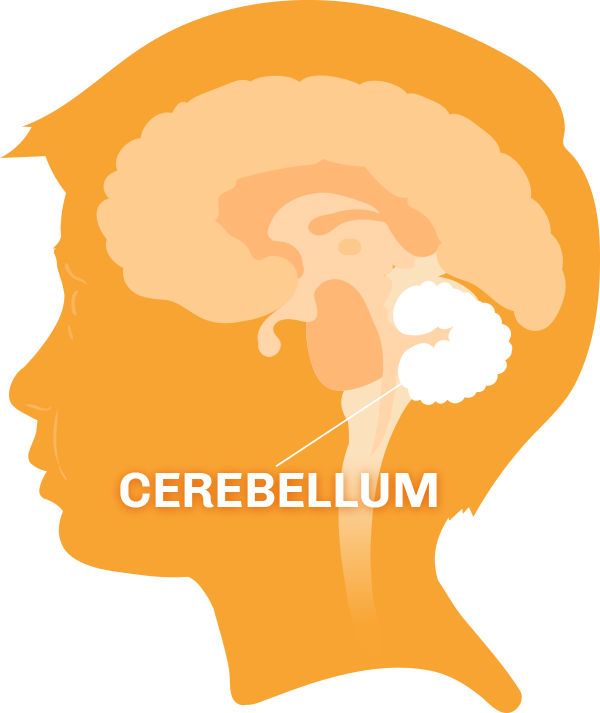
What is Medulloblastoma?
Medulloblastoma is classified as an embryonal tumor, meaning it arises from undeveloped cells in the brain. It typically forms in the cerebellum or posterior fossa, a small, tightly packed space at the base of the skull. Given its location, medulloblastoma can cause significant pressure on the brainstem, leading to a range of neurological symptoms. Despite its aggressive nature, significant advances in treatment have improved survival rates, offering hope to many patients and families.
Common Symptoms of Medulloblastoma
Symptoms of medulloblastoma can vary depending on the size and location of the tumor, as well as the age of the patient. Common signs include:
- Headaches, often worse in the morning or after physical activity
- Nausea and vomiting
- Balance and coordination problems
- Dizziness or difficulty walking
- Vision changes, such as double vision or uncontrolled eye movements
- Seizures (in rare cases)
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of medulloblastoma is not fully understood, but several genetic and environmental factors have been identified as increasing the risk. Known risk factors include:
- Genetic syndromes like Li-Fraumeni syndrome, Gorlin syndrome, and Turcot syndrome
- Family history of brain tumors or certain genetic mutations
- Exposure to ionizing radiation
- In rare cases, certain inherited genetic changes
How Medulloblastoma is Diagnosed
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of neurological exams, imaging studies, and tissue sampling. Key diagnostic tools include:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – to locate the tumor and assess its size and spread
- Computerized Tomography (CT) scans – for a detailed look at brain structures
- Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap) – to check for cancer cells in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- Biopsy or Surgical Resection – to confirm the diagnosis and determine tumor subtype
Treatment Options for Medulloblastoma
Treatment for medulloblastoma is aggressive and typically involves a combination of therapies:
- Surgery – to remove as much of the tumor as safely possible
- Radiation Therapy – often targeted at the brain and spine to kill remaining cancer cells
- Chemotherapy – to target cancer cells throughout the body
Medulloblastoma Survival Rates and Prognosis
The prognosis for medulloblastoma varies depending on several factors, including the patient’s age, tumor subtype, and extent of spread at diagnosis. Five-year survival rates for standard-risk medulloblastoma can be as high as 70-80%, while high-risk cases have poorer outcomes. Early diagnosis and advances in treatment have significantly improved long-term survival rates in recent decades.
Living with Medulloblastoma
Caring for a patient with medulloblastoma can be challenging, but support is available. Resources for families include guidance on managing symptoms, maintaining quality of life, and accessing financial and emotional support. It is also important for survivors to receive ongoing monitoring for potential late effects of treatment, including cognitive, hearing, and endocrine issues.
Ongoing Research and Hope for a Cure
Research into medulloblastoma is ongoing, with scientists exploring targeted therapies, immunotherapy, and genetic treatments aimed at improving survival and reducing long-term side effects. These lab models are helping researchers better understand tumor behavior and genetic changes, with the long-term goal of improving care.