Medulloblastoma Brain Tumor
Medulloblastoma is a rare type of cancer in which a brain tumor forms in the lower back of the brain or in the spinal cord. It is a malignant (cancerous), fast-growing tumor.
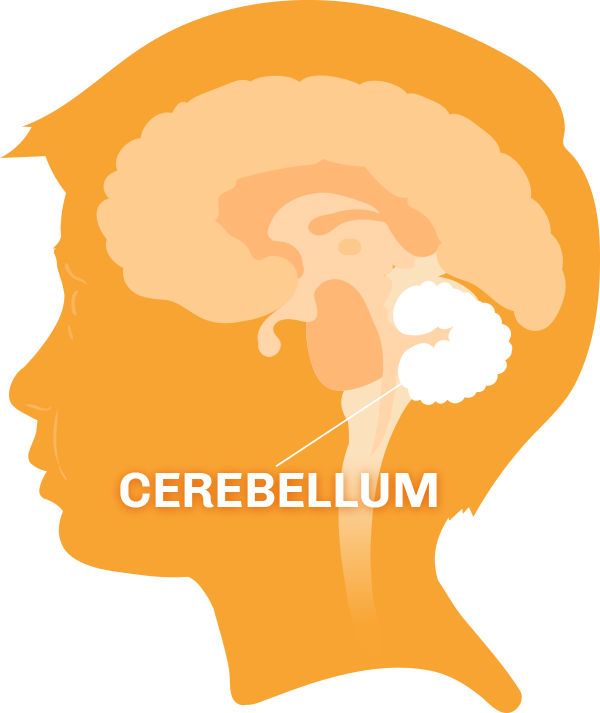
Medulloblastomas occur in the central nervous system (CNS), which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. Most commonly, medulloblastomas are found in an area of the brain called the cerebellum. This is found at the bottom of the brain in the back of the head next to the spinal cord.
Medulloblastoma can spread to other areas of the brain and spine even before diagnosis. It is rare for the tumor to metastasize (grow larger and spread) outside the central nervous system.
The name medulloblastoma describes where the tumor grows and what kinds of cells it's made up of.
Recently Diagnosed With a Medulloblastoma Brain Tumor?
Hearing the diagnosis of medulloblastoma is difficult, but there are steps you can take to improve the quality of care for someone newly diagnosed with medulloblastoma.
Who Is Affected By Medulloblastoma Tumors?
The majority of medulloblastoma cases (70%) are found in children and teens. It is diagnosed most often between the ages of 4-9. When it occurs in adults, it typically appears between ages 20-40.
Medulloblastoma is the most common malignant brain tumor in children, with about 400-500 new diagnoses per year in the United States.
Why Do Certain People Get Medulloblastoma?
The cause of most medulloblastomas is not known. Changes (called mutations) in genes are responsible for the start of all cancers. It is not known in medulloblastoma why these gene changes occur.
A small number of medulloblastomas are related to gene changes that can be passed down in families.
Clinical Signs of a Medulloblastoma Brain Tumor
Most often a person with medulloblastoma will begin to experience one or more of the following symptoms:
- Headaches that may be occasionally relieved by vomiting
- Seizures
- Vision, hearing, and speech problems
- Nausea
- Loss of balance and trouble walking
- Loss of appetite
- Changes in personality, mood or behavior
- Sleepiness
- Weakness
Medulloblastoma Brain Tumor Appearance on MRI
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)> scan is the best noninvasive way to determine the size and properties of brain tumors.
In cases of suspected medulloblastoma, sometimes a computed tomography (CT) scan will be done first. But the best way to evaluate medulloblastoma through imaging is with an MRI of the brain. An MRI of the spine is done as well to see if there is spread of tumor also known as "metastasis."
Once the tumor is removed during surgery, a portion of it will be sent to a lab for testing. That’s what allows your doctor to make a definitive diagnosis of medulloblastoma.
Clinical Course for Medulloblastoma
After MRI diagnosis of medulloblastoma, a typical sequence of events is as follows:
- Possible temporary external ventricular drain (EVD) placed to relieve hydrocephalus (if severe)
- Hydrocephalus is a condition that occurs when too much cerebrospinal fluid builds up in the brain. This buildup causes harmful pressure in the brain. The pressure can be relieved with an EVD or a shunt (mentioned below).
- Surgery to remove the tumor (also called tumor resection)
- Possible permanent ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt placement or endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) if hydrocephalus cannot resolve
- Treatment with radiation and/or chemotherapy